Example
- Example (The Sample Mean)
- Let
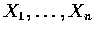 be independent and identically distributed random variables
having distribution function F and expected value
be independent and identically distributed random variables
having distribution function F and expected value 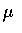 .
Such a sequence of
random variables is said to constitute a sample from the distribution F. The
quantity
.
Such a sequence of
random variables is said to constitute a sample from the distribution F. The
quantity
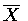 ,
defined by
is called the sample mean. Compute
,
defined by
is called the sample mean. Compute
![$E[\overline{X}]$](img5.gif) .
.
- Solution:
-
That is, the expected value of the sample mean is
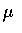 ,
the mean of the
distribution. When the distribution mean
,
the mean of the
distribution. When the distribution mean 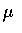 is unknown, the sample mean is
often used in statistics to estimate it.
is unknown, the sample mean is
often used in statistics to estimate it.
- Example (Boole's Inequality)
- 令
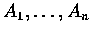 為 n 個事件且定義指標變數
為 n 個事件且定義指標變數
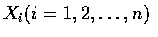 如下:
令
如下:
令
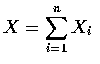 .
故 X 表示事件 Ai 發生的個數. 最後, 令
也就是說, 當至少有一事件 Ai 發生時, Y 等於 1, 否則 Y 為 0.
因
.
故 X 表示事件 Ai 發生的個數. 最後, 令
也就是說, 當至少有一事件 Ai 發生時, Y 等於 1, 否則 Y 為 0.
因 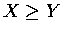 故
故
![$ E[X] \geq E[Y] $](img14.gif) 但是因為
但是因為
![$ E[X] = \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n E[X_i] = \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n P(A_i) $](img15.gif) 且
所以我們得到 Boole 不等式, 即
且
所以我們得到 Boole 不等式, 即
![$P \left ( \displaystyle\bigcup_{i=1}^n A_i\right ) \leq\sum_{i=1}^n P(A_i)\qquad\rule[0.02em]{1.0mm}{1.5mm}$](img17.gif)
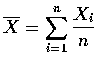
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
E[\overline{X}]&=&E\left [\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n\frac{X_i...
...1}^nE[X_i] \\ \\
&=&\mu \qquad\qquad\mbox{ since } E[X_i]\equiv\mu
\end{array}$](img6.gif)
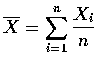
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
E[\overline{X}]&=&E\left [\displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n\frac{X_i...
...1}^nE[X_i] \\ \\
&=&\mu \qquad\qquad\mbox{ since } E[X_i]\equiv\mu
\end{array}$](img6.gif)
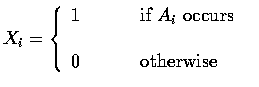
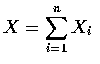 .
故 X 表示事件 Ai 發生的個數. 最後, 令
.
故 X 表示事件 Ai 發生的個數. 最後, 令
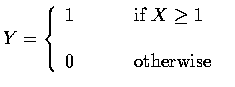
![$ E[X] = \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n E[X_i] = \displaystyle\sum_{i=1}^n P(A_i) $](img15.gif) 且
且
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
E[Y]&=&P\{\mbox{at least one of the } A_i \mbox{ occur}\} \\ \\
&=&P\left (\displaystyle\bigcup_{i=1}^n A_i \right )
\end{array}$](img16.gif)
![$P \left ( \displaystyle\bigcup_{i=1}^n A_i\right ) \leq\sum_{i=1}^n P(A_i)\qquad\rule[0.02em]{1.0mm}{1.5mm}$](img17.gif)