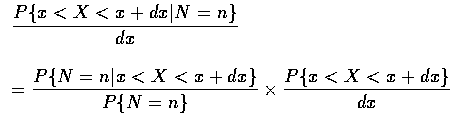
Conditional Distribution - Continuous Case and Discrete Case
當隨機變數不是聯合連續隨機變數也不是聯合離散隨機變數時, 我們也可討論隨機變數的條件分布. 例如, 設 X 為一連續隨機變數, 其機率密度函數為 f, 而 N 為一離散隨機變數, 現在考慮在給予 N=n 的條件下, X 的條件分布函數. 因為
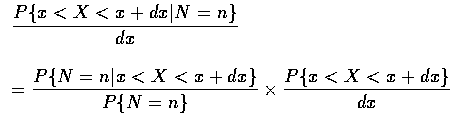
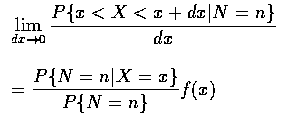
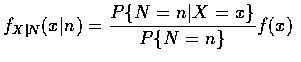
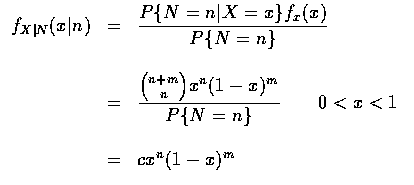
The above result is quite interesting, for it states that if the original or
prior (to the collection of data) distribution of a trial success
probability is uniformly distributed over (0,1) [or, equivalently, is beta
with parameters (1,1)] then the posterior (or conditional) distribution given
a total of n successes in n+m trials is beta with parameters (1+n,1+m).
This is valuable, for it enhances our intuition as to what it means to assume
that a random variable has a beta distribution.