Proposition
Proposition
設
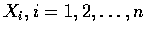 為獨立隨機變數, 且都具有常態分布,
其參數分別為
為獨立隨機變數, 且都具有常態分布,
其參數分別為
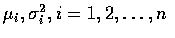 則
則
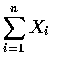 為參數是
為參數是
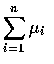 和
和
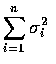 的
常態隨機變數.
的
常態隨機變數.
- Example (Sums of Independent Poisson Random Variables)
- 設 X 和 Y 為獨立卜瓦松隨機變數, 其參數分別為
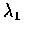 和
和
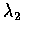 ,
試求 X+Y 的分布.
,
試求 X+Y 的分布.
- Solution:
- 因為事件
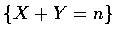 可寫成互斥事件
可寫成互斥事件
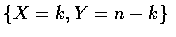 的聯集,
其中
的聯集,
其中
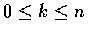 ,
故得
也就是說, X+Y 為參數是
,
故得
也就是說, X+Y 為參數是
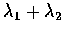 的卜瓦松隨機變數.
的卜瓦松隨機變數.
![$\rule[0.02em]{1.0mm}{1.5mm}$](img13.gif)
- Example (Sums of Independent Binomial Random Variables)
Let X and Y be independent binomial random variables with respective
parameters (n,p) and (m,p). Calculate the distribution of X+Y.
[Solution:
- Without any computation at all we can immediately conclude, by recalling the
interpretation of a binomial random variable, that X+Y is binomial with
parameters (n+m,p). This follows because X represents the number of
successes in n independent trials, each of which results in a success with
probability p; similarly, Y represents the number of successes in mindependent trials, each trial being a success with probability p. Hence, as
X and Y are assumed independent, it follows that X+Yrepresents the
number of successes in n+m independent trials when each trial has a
probability p of being a success. Therefore, X+Y is a binomial random
variable with parameters (n+m, p). To check this result analytically, note
that
where q=1-p and where
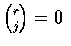 when j>r. Hence
and the result follows upon application of the combinatiorial identity
when j>r. Hence
and the result follows upon application of the combinatiorial identity
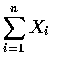 為參數是
為參數是
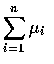 和
和
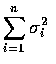 的
常態隨機變數.
的
常態隨機變數.
![]() 為獨立隨機變數, 且都具有常態分布,
其參數分別為
為獨立隨機變數, 且都具有常態分布,
其參數分別為
![]() 則
則
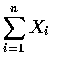 為參數是
為參數是
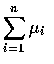 和
和
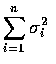 的
常態隨機變數.
的
常態隨機變數.
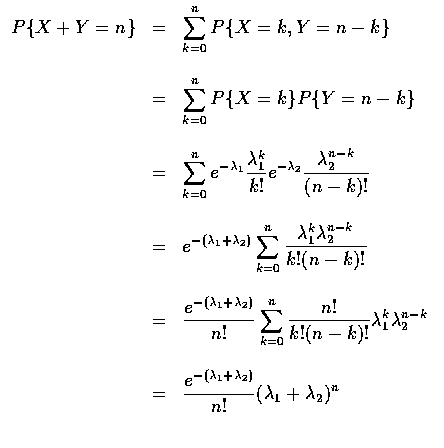
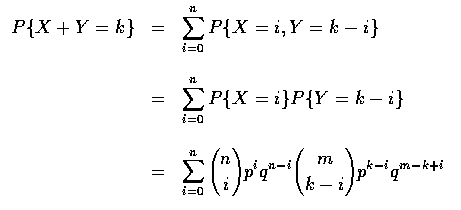
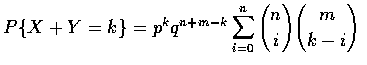
![${n+m\choose k}=\displaystyle\sum_{i=0}^n{n\choose i}{m\choose k-i}\qquad\rule[0.02em]{1.0mm}{1.5mm}$](img18.gif)