Independent of n random variables
當然, 獨立的概念也可適用於兩個以上的隨機變數. 一般而言, 若對所有的實數集合
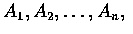
則稱此 n 個隨機變數
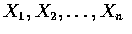 為獨立隨機變數. 與前面一樣,
可證得此條件相當於 : 對所有的實數
為獨立隨機變數. 與前面一樣,
可證得此條件相當於 : 對所有的實數
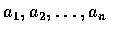 ,
最後, 對一無窮序列的隨機變數而言, 若它的任意有限子集合均為獨立的話,
則稱此無窮序列的隨機變數為獨立.
,
最後, 對一無窮序列的隨機變數而言, 若它的任意有限子集合均為獨立的話,
則稱此無窮序列的隨機變數為獨立.
- Example
- Let X,Y,Z be independent and uniformly distributed over (0,1). Compute
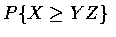 .
.
- Solution:
- Since
fX,Y,Z(
x,
y,
z)=
fX(
x)
fY(
y)
fZ(
z)=1
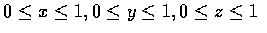
we have
![]()
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
P\{X\geq YZ\}&=&\displaystyle\int\int\int\limits_{\hspace{-0...
...\ \\
&=&\displaystyle\frac{3}{4} \qquad\rule[0.02em]{1.0mm}{1.5mm}
\end{array}$](img8.gif)