Multinomial Distribution
我們可以利用與兩個隨機變數完全同樣的方法來定義 n 個隨機變數的聯合機率分布.
例如, n 個隨機變數
![]() 的聯合累積機率分布函數
的聯合累積機率分布函數
![]() 的定義為
的定義為
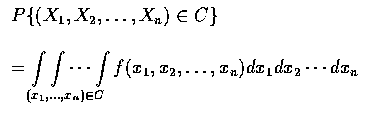
則稱此 n 個隨機變數為聯合連續隨機變數; 而
![]() 則稱為它們的聯合機率密度函數. 特別當
則稱為它們的聯合機率密度函數. 特別當
![]() 為 n 個實數集合時,
為 n 個實數集合時,
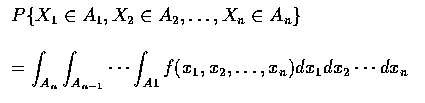
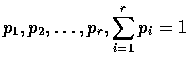 .
If we denote by Xi, the number of the n experiments that result in outcome
number i, then
.
If we denote by Xi, the number of the n experiments that result in outcome
number i, then
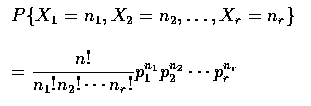
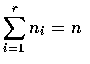 .
.
UP equation is verified by noting that any sequence of outcomes for the nexperiments that leads to outcome i occurring ni times for
![]() will, by the assumed independence of experiments, have
probability
will, by the assumed independence of experiments, have
probability
![]() of occurring. As there are
of occurring. As there are
![]() such sequences of outcomes (there are
such sequences of outcomes (there are
![]() different permutations of n things of which n1are alike, n2 are alike, ... , nr are alike), up equation is established.
The joint distribution whose joint probability mass function is specified of up,
is called the multinomial distribution. When r=2, the multinomial readuces to
the binomial distribution.
different permutations of n things of which n1are alike, n2 are alike, ... , nr are alike), up equation is established.
The joint distribution whose joint probability mass function is specified of up,
is called the multinomial distribution. When r=2, the multinomial readuces to
the binomial distribution.
![]()