前面所講的假設都是屬於單邊的假設 one-sided hypotheses, 在對立假設中,
![]() 相對於虛無假設都是只有單邊的, 對於檢定則稱為單邊檢定或單尾檢定
(one-sided tests or one-tailed tests).
相對於虛無假設都是只有單邊的, 對於檢定則稱為單邊檢定或單尾檢定
(one-sided tests or one-tailed tests).
上面的假設則稱為雙邊的假設(two-sided alternative), 假如
![]() 距離
距離
![]() 太遠的話則拒絕 H0 的假設, 也就是 Z 太小或太大. 給定
太遠的話則拒絕 H0 的假設, 也就是 Z 太小或太大. 給定 ![]() 即可決定棄卻域, 如下,
即可決定棄卻域, 如下,
Large Sample Tests for ![]()
When the sample size is large, a Z-test concerning ![]() is based on the
normal test statistic
is based on the
normal test statistic
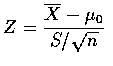
The rejection region is one- or two-sided depending on the alternative hypothesis. Specifically,
