具備以機率分配作為測度的有效模式的概念以及具有抽樣分配的相關概念,
接著介紹推論的方法. 當從一全體中抽樣得到資料時,
統計分析的最重要目的是從包含於樣本資料中的部份訊息來導出關於全體的推論或一般性.
- Statistical inference
- Statistical inference deals with drawing conclusions about population
parameters from an analysis of the sample data.
The two most important types of inferences are (1) estimation of
parameter(s) and (2) testing of statistical hypotheses.
- estimation of parameters
- The true value of a parameter is an unknown constant that can be correctly
ascertained only by an exhaustive study of the population, if indeed that were
possible. Our objective may be to obtain a guess or an estimate of the unknown
true value along with a determination of its accuracy. This type of inference is
called estimation of parameters.
- testing of statistical hypotheses
- An alternative objective may be to examine whether the sample data support or
contradict the investigator's conjecture about the true value of the parameter.
This latter type of inference is called testing of statistical hypotheses.
- 例
- 假如我們想要研究松樹早期的生長比率, 計錄下 40 株小松苗的高度,
由計錄所得到的觀察值, 我們對於 "平均高度" 以及真正的可能值有興趣.
也就是我們對於未知的
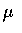 有興趣, 可作下列的推論.
有興趣, 可作下列的推論.
- 點估計
- Estimate a single value for the unknown
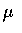 (point
estimation).
(point
estimation).
- 區間估計
- Determine an interval of plausible values for
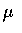 (interval estimation).
(interval estimation).
- Hypothesis
- Decide whether or not the mean height
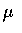 is 1.9
centimeters,which was previously found to be the mean height of a different
stock of pine seedlings (testing a hypothesis).
is 1.9
centimeters,which was previously found to be the mean height of a different
stock of pine seedlings (testing a hypothesis).
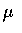 (point
estimation).
(point
estimation).
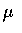 (interval estimation).
(interval estimation).
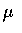 is 1.9
centimeters,which was previously found to be the mean height of a different
stock of pine seedlings (testing a hypothesis).
is 1.9
centimeters,which was previously found to be the mean height of a different
stock of pine seedlings (testing a hypothesis).