The normal approximation to the binomial applies when n is large and the
success probability p is not too close to 0 or 1. The binomial probability of
![]() is approximated by the normal probability of
is approximated by the normal probability of
![]() .
.
When np and n(1-p) are both large, say, greater than 15, the binomial
distribution is well approximated by the normal distribution having
![]() and
and
![]() .
That is,
.
That is,
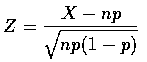 is approximately N(0,1)
is approximately N(0,1)
假設隨機變數 X 為 1000 位成年人中長期飲運含有酒精成份飲料的人數.
則在所占比例 30% 的假設下, X 為
n=1000,p=.3 的二項分配, 也就是說
![]() ,
因此
,
因此
意思是說 X 的分配趨近於 N(300,14.49).
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
P[X\leq 279]&\approx&\displaystyle P[Z\leq\frac{279.5-300}{14.49}] \\ \\
&=&P[Z\leq -1.415] \\ \\
&=&.0786 \\ \\
\end{array}$](img9.gif)
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
P[X\geq 316]&\approx&\displaystyle P[Z\geq\frac{315.5-300}{14.49}] \\ \\
&=&P[Z\geq -1.07] \\ \\
&=&1-.8577=.1423 \\ \\
\end{array}$](img10.gif)