If X is distributed as
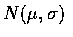 ,
then the standardized variable
,
then the standardized variable
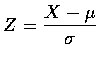 has the standard normal distribution. This
property of the normal distribution allows us to cast a probability problem
concerning X into one concerning Z. To find the probability that X lies in
a given interval, convert the interval to the z-scale and then calculate the
probability by using the standard normal table.
has the standard normal distribution. This
property of the normal distribution allows us to cast a probability problem
concerning X into one concerning Z. To find the probability that X lies in
a given interval, convert the interval to the z-scale and then calculate the
probability by using the standard normal table.
If X is distributed as
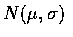 ,
then
,
then
where Z has the standard normal distribution.
- 例
- The number of calories in a salad on the lunch menu is normally distributed
with mean=200 and sd=5. Find the probability that the salad you select will
contain
- (a)
- More than 208 calories.
- (b)
- Between 190 and 200 calories.
Letting X denote the number of calories in the salad, we have the standardized
variable
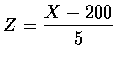
- (a)
- The z-value corresponding to x=208 is
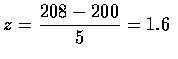 .
Therefore,
.
Therefore,
- (b)
- The z-values corresponding to x=190 and x=200 are
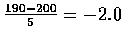 and
and
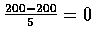 respectively. We calculate
respectively. We calculate
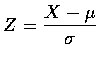 has the standard normal distribution. This
property of the normal distribution allows us to cast a probability problem
concerning X into one concerning Z. To find the probability that X lies in
a given interval, convert the interval to the z-scale and then calculate the
probability by using the standard normal table.
has the standard normal distribution. This
property of the normal distribution allows us to cast a probability problem
concerning X into one concerning Z. To find the probability that X lies in
a given interval, convert the interval to the z-scale and then calculate the
probability by using the standard normal table.
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
\displaystyle P[a\leq X\leq b]&=&P[\displaystyle\frac{a-\mu}...
...frac{b-\mu}{\sigma}]-P[\displaystyle Z\leq\frac{a-\mu}{\sigma}] \\
\end{array}$](img3.gif)
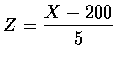
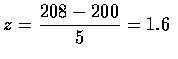 .
Therefore,
.
Therefore, ![$\begin{array}{rcl}
P[X>208]&=&P[Z>1.6] \\
&=&1-P[Z\leq 1.6] \\
&=&1-.9452=.0548 \\
\end{array}$](img7.gif)
![$\begin{array}{rcl}
P[190\leq X\leq 200]&=&P[-2.0\leq Z\leq 0] \\
&=&.5-.0228=.4772 \\
\end{array}$](img10.gif)